I've had a number of emails recently asking after our blankets in the library at the University of York, so I thought I'd blog about them.
Getting blankets for the library is probably one of the best things I've ever done in libraryland, honestly. It took almost no effort and very little money. The students LOVE them. Everyone's a winner.
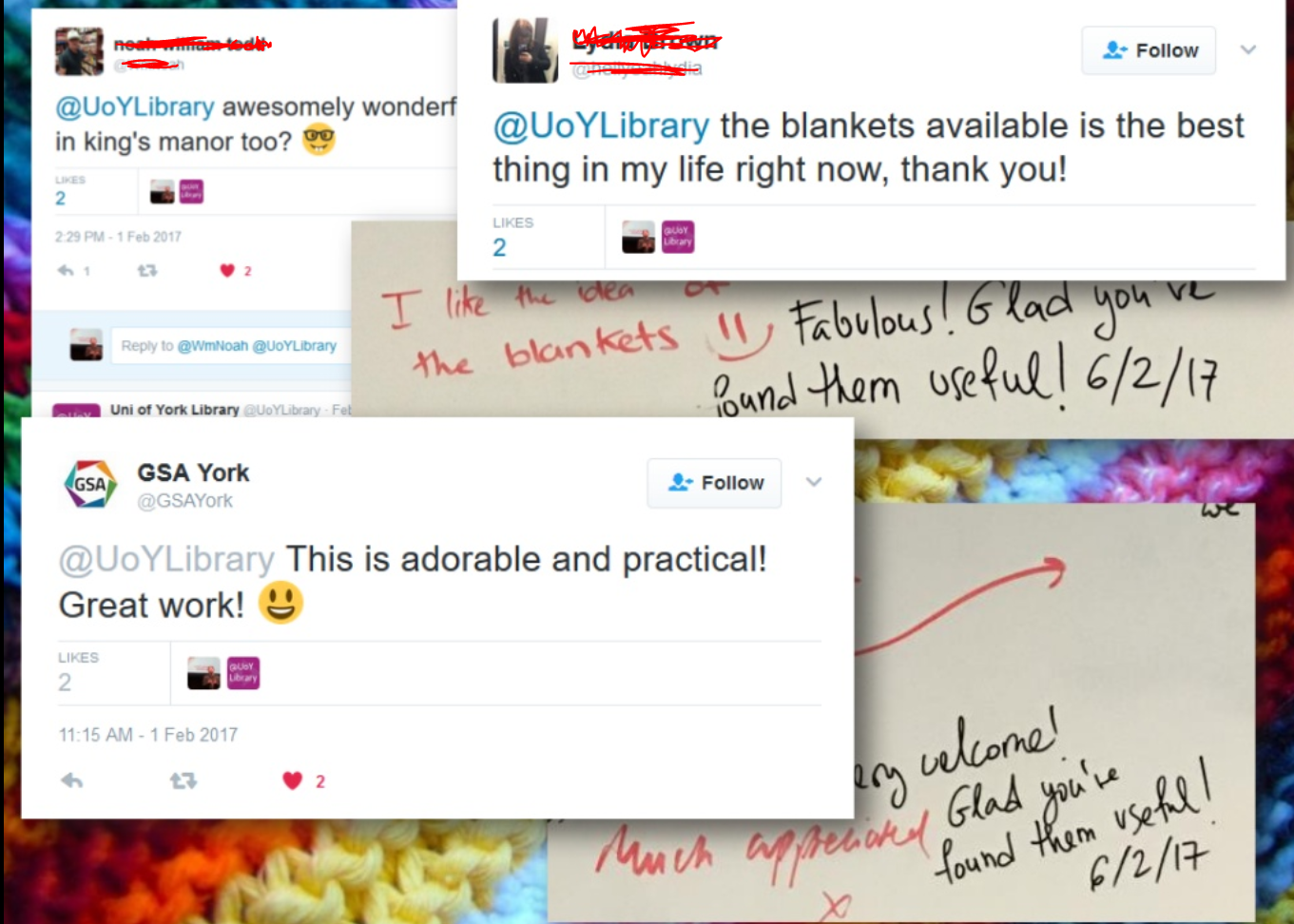
The quote in the title is from our feedback board where we asked students for tips for their peers. Here are some other quotes from the Graffiti Wall and from Twitter:
A plethora of positive feedback for the blankets
So the tl;dr of this post is, get blankets in your library! It's 100% worth doing.
Practicalities
We bought 30 blankets for each of our sites. We get them from a local laundry who also launder them for us - but you can also buy perfectly serviceable and cheap examples from for example IKEA if you have your own laundry service to hand. They're laundered termly unless there's a reason to bring that schedule forward...
They sit in a bucket near the entrance of each library, and people can help themselves to them as they come and go. Here's a picture of the main campus library blankets:
You'll notice the blankets are a fairly drab grey - this is deliberate, to make them less tempting to abscond with...
Origins
Like all academic libraries, our number 1 complaint for users is about the temperature - and it's equally split between too hot and too cold most of the time. We don't actually control the temperature anyhow, so we adopted the UX mentality of 'if you can't fix the problem at least make the user experience better in any way you can' and tried to improve things in what small ways we could.
We'd heard at UXLibs I that a college in Cambridge had given out blankets and that this had reduced their complaints about the cold. Some students of mine from the History of Art Department came to me as part of Library Committee and told me it was basically too cold to work in Kings Manor, our town centre site which is in a building several hundred years old, so I immediately thought back to what Cambridge had done and resolved to steal their idea... (Sonya Adams and Libby Tilley at Cambridge were both really helpful to me in advising on how to set this whole thing up.)
The students involved were really pleased but the great thing is EVERYONE was really pleased.
So as we head into the colder months, see if you can do this for your library. Or even better, get your students SLANKETS so their arms are still free for reading. :)