There's a very famous Neil Gaiman quote among librarians and lovers of libraries: "Google will bring you back, you know, a hundred thousand answers. A librarian will bring you back the right one."
You see it on social media. You hear it used as a soothing balm at library conferences. More than one library has it printed on their floors.
There are various different versions of the quote - often people will attribute Gaiman with having said a million answers from Google, and pretty much no one puts in the 'you know'. In order that I, a librarian, could use the RIGHT quote for this article I...
Well, I Googled it. Obvs.
Because how else would I find it? I don't want to put us as libraries and librarians in competition with Google for loads of reasons, but we still do it a lot. I contributed to a SWOT analysis on libraries in LibFocus and someone put the Gaiman quote in there too:
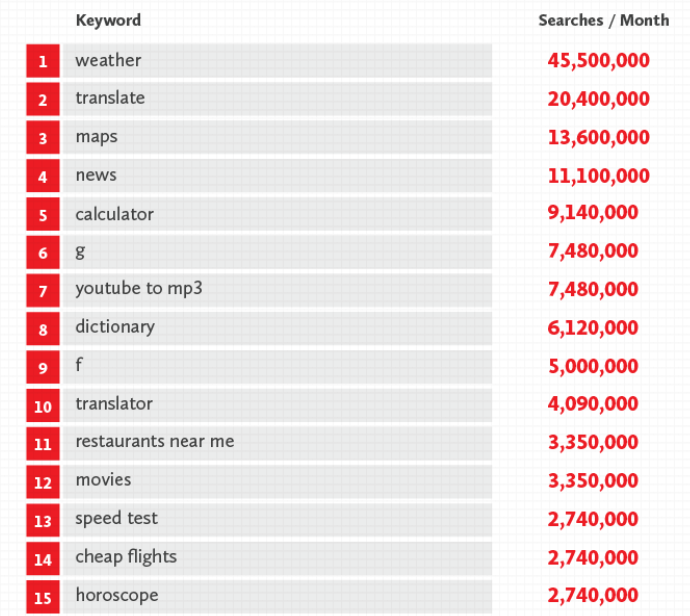
The thing is, most people aren't seeking 'right answers' on Google. They just want basic or general info. Here's what SiegeMedia discovered were the top 15 searches on Google in 2015 in the US, if you exclude brands and porn (the top 5 if you don't exclude them is Gmail, Craiglists, Amazon, Yahoo [why?!] and porn).
How many of those have a right answer a librarian could bring back? The weather, obviously - but you'd find that out by Googling it. Perhaps a librarian could find you a more reliable dictionary, that could be a 'right' answer. What's on at the Movies, cheap flights - again we'd at least go online and search, if not specifically Google.
In the UK in 2015 according to Google itself, the top 5 searches were 1) Cilla Black, 2) Lady Colin Campbell, 3) Rugby World Cup, 4) Jeremy Clarkson and 5) Paris. Is there a right answer to 'Cilla Black'? Right answers are not what Google is for. More broadly, people aren't searching Google for things they used to come and find at libraries.
The reason the Gaiman quote includes a 'you know' is this wasn't some grand written statement, it was part of an answer to an interview question he was asked upon becoming honorary chair of National Libaries Week in 2010. The full answer, with the Google part right at the end, can be seen in this video:
What a great quote that whole thing is! Fantastic. He GETS it. This isn't some well-meaning but misguided celeb talking about how much they loved the smell of books as a child in their local library. This is someone who understands how libraries are about social inclusion. I love the full answer. I think Gaiman is brilliant. I just wish we, as a library community, hadn't quite latched onto the Google part of it so much, as the dichotomy isn't helpful.
Also, I don't personally think I can find the 'right' answer in most of the situations I find myself in, even as an academic librarian helping people are who ARE actually after very specific information. Our role is more about helping people find answers for themselves - not in all cases and branches of the profession, but in most - as a couple of people pointed out on Twitter:
@ned_potter Neither would I ever claim to be offering a 'right' one.
— Clare McCluskey Dean (@claremcdean) November 3, 2016
@ned_potter @libfocus wow! no pressure on librarians so. I thought we were empowering people to find answers for themselves.
— Lorna Dodd (@LornaDodd) November 3, 2016
Of course this dichotomy isn't somehow Gaiman's fault or exclusive to him, you see it everywhere among librarians. This tweet from Internet Librarian International encapsulates a sentence you hear a lot about libraries and competition:
Our competition are your googles, apples, amazons who are doing a great (better?) job of what we in libraries do #ili2016 #challenge
— Martin O'Connor (@martinoconnor3) October 19, 2016
(It was reflecting something the speaker had said rather than Martin's own opinion.) I find this rhetoric troubling for lots of reasons, many of which I've spoken about before but the idea of Google as competitor just won't go away...
Here are my issues with it:
- As discussed above, people don't now use Google for things they previously used libraries for
- Google doesn't do what we do. It precisely the human element of libraries that will ensure they endure
- If Google IS our competitor then we will lose every battle, forever
- Ultimately, to pit libraries against Google is to reduce libraries to their most basic function (provider of information) and indeed the one which IS most easily replaced...
- ... and then try and convince people not to replace us with Google by telling them Google is not any good, when in fact - for all the troubling things about Google, and there are many - it IS pretty good at bringing back info of sufficient quality that most people who are non-specialists find it to be excellent for their needs
- Related: no one ever won any friends by slagging off something useful (that they themselves use every day)
The fact that Google and the internet more widely has made it so easy for people to access information without needing to physically visit a library is a GOOD thing. So I'd like us all agree to stop trying to make it into us versus them, and focus more on the things we can do to cater for the needs of our users and potential users. They don't need us to find them info on Cilla Black but they DO need us for plenty else.
Google could find 100,000 things for libraries to do next, but only our communities can find us the right one...